
Dear students, Welcome to Structures II! Get ready to explore the fundamentals of designing structural elements and systems using timber and composite materials. I am excited to guide you through this learning journey. Let’s work together to deepen your understanding and skills in structural design.
1. Module Aim
This module is designed to study the design of structural elements and systems using timber. It focuses on loaded members such as beams, columns, and trusses under axial, shear, bending, and combined loading. The course also covers composite structures combining timber and steel, including their connections.
2. Expected Outcomes
By the end of the Structures II course, students will be able to:
-
Design Timber Structural Elements: Create designs for elements loaded under axial, shear, bending, and combined loading.
-
Understand Composite Structures: Analyze and design connections between timber and steel in composite structures.
-
Apply Design Methods: Implement techniques to design timber-loaded members such as beams, columns, and trusses.
-
Integrate Structure into Architecture: Apply structural concepts into the architectural studio design of structural forms.
-
Analyze Structural Elements: Evaluate and check different building elements and components against various loading conditions.
-
Select Architectural Forms: Choose appropriate architectural forms during the design of buildings.
-
Engage in Self-Learning: Independently advance knowledge in the field of structures.
-
Produce Structural Reports: Write simple reports describing the behavior of structural elements.
- Teacher: Felicien MATABARO
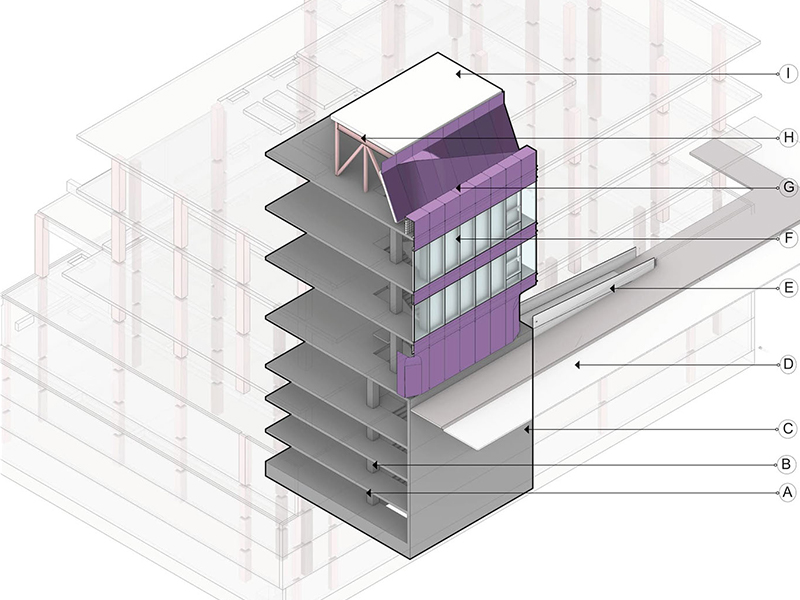
The course of Building Technology II expends the practical skills learnt in Building Technology I and deepen the skills related to construction of buildings. The course aims to provide the principles of Building Technology as applied to Engineering practice. It covers framed structures, Suspended floors and Concrete Structures. It therefore gives details about any of considered structures.
Having successfully completed the module, students should be able to
demonstrate knowledge and understanding of:
i. Framed structures, such as multi-storey frames
ii. The various types of building materials, their properties, and performance.
iii. the principles of various manufacturing, fabrication, and construction processes needed for realizing necessary Architectural designs and construction
iv. The fundamental principles in construction management, maintenance and quality control.
v. Tentatively evaluate building work that has been carried out by other professionals
vi. Select suitable emerging building materials and techniques, and also appropriate technologies in construction
vii. Identify suitable building roof shapes for a selected safe site and building function.
viii. Elaborate building Elements and components details applicable to the building construction
ix. Implement and supervise as well as coordinate consultant inputs into the construction of all building structures, while guiding the contractors and suppliers and other technical staff on the job.
x. Prepare technical reports and deliver technical presentations.
- Teacher: ogbole gregory anthony ogah

The course aims to study provision of water such as basic cold water, hot water supply, storage, distribution and drainage. It introduces electrical installation, wiring facilities, ducts, etc. Also fire protection such as means of escape, fire regulations, grading, resistance and detection systems. The talks about refuse disposal systems such as chutes, incinerator, gauchely systems, and macerator equipment. mechanical systems, pumps sizes and location. Provision of specialized services such as lifts, escalators and air conditioning are finally considered.
Having successfully completed the module, students should be able to demonstrate knowledge and understanding of:
i. Provision of water in a building
ii. Electrical installation and wiring facilities
iii. Ducts and fire protection
iv. Refuse disposal systems
v. Mechanical systems, pumps sizes and location and
vi. Provision of specialized services such as lifts, escalators and air conditioning:
vii. tentatively evaluate work that has been carried out by other professionals, that about Provision of water in the Building, electrical installation, etc.
viii. Supervise small project of water provision, electrical installation, wiring facilities, fire protection, refuse disposal systems and mechanical systems for a selected site of construction.
ix. conduct such works as Water provision, Fire protection system installation.
x. Supervise small building works about the above mentioned areas.
xi. Undertake self learning in Building technology
xii. Produce reports about Construction Works.
- Teacher: ogbole gregory anthony ogah

This course introduce the Design in Urban and Rural Contexts. The studio will present students with two projects of similar program in two different environments on real sites in East Africa; one in an urban setting and one in a rural setting. Students will investigate appropriate solutions using the similarities and differences of the two settings. Response to the local context and sustainable design solutions will be emphasized. Students will be immersed in a studio environment and will be instructed through individual critiques and group pin-ups. At the end of this course, students will be able to cope with the design challenges
Having successfully completed the module, students should be able to demonstrate knowledge and understanding of:
i. Identifying appropriate design strategies in two different contexts.
ii. The design challenges unique to each particular setting.
iii. Different design solutions to similar problems as influenced by local context.
iv. Design different architectural objects according to differing contextual situations.
v. Deal with issues of sustainability in different settings.
vi. Apply precedents and research to design work.
vii. Produce coherent and thoughtful solutions to multiple design problems.
viii. Effectively present projects to an interdisciplinary audience.
ix. Learn independently in familiar and unfamiliar situations with open mindedness and in a spirit of critical enquiry.
x. Communicate ideas visually and verbally in a presentation format.
xi. Demonstrate an ability to develop spatial and systematic solutions to complex problems.
This module explores African traditional culture and context and its influence on styles and languages of architecture examines the spatial, formal and structural components of select case studies from various parts of Africa.
Having successfully completed the module, students should be able to:
i. Describe different styles of African architecture and identify significant moments and attributes in this period of architectural history
ii. Illustrate how these communities responded to functional, aesthetic and structural
iii. Identify and give an account of the major design styles and movements from African antiquity
iv. Demonstrate an understanding of the context and development of the various styles
v. demonstrate a familiarity with the basic geographical and chronological framework of the various case studies
vi. portray a thorough understanding of inherent architectural issues and are able to express these ideas in a structured and coherent way
vii. Demonstrate skill and confidence in ordered and coherent expression, both written and spoken
viii. Learn independently in familiar and unfamiliar situations with open mindedness and in a spirit of critical enquiry.
ix. Work constructively as a member of a team and to manage both time and other sources effectively to meet the deadlines.
x. Demonstrate general numerical skills and problem solving skills.

The coursework will provide students with the basic skills for regional and local site analysis, introduction to landscape design methods, and graphic and model representation, including site plan, section, elevation, and sketching. Sustainable landscape solutions will be reviewed based upon the understanding that a landscape is designed to address ecological, economic, and social contexts to both meet the needs of society and minimize negative impacts on the future environment.
Having successfully completed the module, students should be able to demonstrate knowledge and understanding of:
i. Impact of ecology, hydrology, climate, exposure, flora, fauna, erosions factors, human ecologies, and economic contexts at various site scales from regional to local.
ii. Potential relationship between landscape and built form.
iii. Evaluate existing site landscape processes and potential impacts of various landscape approaches.
iv. Develop graphic communication skills to represent landscape design at various scales of intervention, from regional planning, to small site design.
v. Apply principles of sustainable landscape design to a project site.
vi. Apply design approaches for paving, water management, create plant lists, and represent landscape design.
vii. Apply various basic design approaches to landscape design, including revealing, connecting, insertion, choreography, etc.
viii. Create basic site design, planting, paving documents.
ix. Apply site research to landscape design and detailing.:
x. Learn independently in familiar and unfamiliar situations with open mindedness and in a sprit of critical enquiry.
xi. Work constructively as a member of a team and to manage both time and other sources effectively to meet the deadlines.
xii. Demonstrate general analytical, design, and problem solving skills.

